An Introduction to Letter Writing
- With the advent of emails and modern technology, the concept of writing Letters has taken a back seats but the style persists and people use it while writing emails. Drafting Letters demands meticulous attention. One should be careful about what is being written.
- Following are some objectives of letters writing
Types of Letter
Letters are categorized into two types1. Informal Letters
- These are also known as personal letters, usually written to family, friends, relatives, neighbours or to acquaintances. These letters may or may not have a concrete reason of writing. They may be written just to share an experience, enquire about someone’s how about, updating someone with a general incident etc. In these letters we cover personal letters (letters to family, letters to relatives, love letters and letters to elderly people) and social letters (letters to friends, social invitations, congratulatory/apology letters, letters of condolence/sympathy, thank you letters).
2. Formal Letters
- These letters are written to discuss business, apply for services, make requests, file/register complaints etc. The foundation of these letters and categorization depends upon what is being discussed in the letters. The Letters are short and to the point. The formulation of formal letters, letters of application, official letters and letters to the Editor.
Format of a Letter
- A letter is Composed of various elements that may change depending upon the nature of the letter. The main elements of a letter are given below
Senders’ Address
- Senders; address is the mailing address of the sender. It is an essential part of both, formal and informal letters. It is also known as the return address as it acts as a back up address incase the letter gets damaged or unaccepted.
- It is omitted only if the letter, is being written/typed on a letterhead or stationery already imprinted with the same.
- Senders; address follows a typical format of writing as given below that consists of the designation of the sender (optional) followed by the name of the organization, building numbers, street/area, state/town, pin code and name of the country (if corresponding internationally).
- In case of a business letter, a reference number may also be included depicting that the letter is written in response to a particular enquiry, letter, file, record etc.
- Note Designation of the sender, name of the organization and reference number are not included in the formation of sender’s address of informal lrtters for obvious reasons.
- Line 1 Designation of the sender (optional) (formal letters)
- Line 2 Name of the organization (formal letters)
- Line 3 Building number, street/area (formal letters)
- Line 4 State/town (pin code-optional)
- Line 5 Country (if corresponding internationally)
- Line 6 Reference number (if applicable)
| Formal letter The Manager ABC Pvt. Ltd 23, Wazirpur New Delhi-110005 India Ref no 229/3A/20XX |
Informal letter 23, Wazirpur New Delhi-110005 India |
Date
- Succeeding the space after the return address comes the date on which the letter is written/sent. One may opt any format out of the two stated below to record the date in the letter.
- DD/MM/YY : 24th August, 20XX
- MM/DD/YY : August 24th, 20XX
Receivers’ Address
- Receivers’ address is the corresponding address of the person to whom the letter is being sent. It is placed after the date in formal letters. Since personal letters are sent to acquaintances or known people, receivers’ address is only mentioned on the envelope carrying the letter.\
- If the letter is being addressed to someone whose title/post/name of the official and name of the organization is known, then the sender must start with the receivers’ designation and name of the organization followed by the building numbers, street/area, state/town, pin code (optional) and country (if corresponding internationally) as formatted tittle
- Line 1 Name of the official/professional title
- Line 2 Name of the organization
- Line 3 Building number, street/area
- Line 4 State/town (pin code-optional)
- Line 5 Country (if corresponding internationally)
| The Manager Ecotech Pvt Ltd 19/B2 Pitampura New Delhi – 110077 India |
Subject
- A Subject determines the purpose of writing in the brief. It help the recipient to deal successfully with the aim of yours letter. It is preceded with the word subject and is placed directly after the receivers’ address.
- It is part of formal business letters which are written either in reference to an earlier in reference to an earlier correspondence or to someone with whom the sender is usually in contact. You must have written a subject at least once while applying for leave concession, filing a complaint, executive a deal etc. It should clear, Concise not than 10 words.
Salutation
- The salutation is a customary greeting to the recipient of the letter. It varies depending upon the intimacy/relationship between the sender and the receiver. It usually begins with the word ‘Dear’ followed by the title (Ms/Mrs/Mr/Dr) if know and the first name of the person.
- Incase the gender and name of the recipient is not known you must address the person as Dear Sir/Dear Madam, Since the salutation is professional in formal letters. The salutation used in personal or informal letters is friendly.
- You may greet the receiver as ‘Dear/Dearest’ followed by their first name/nick name. it is advisable to greet your elders with respect such as Dear Grandma/Dear Grandfather etc and not use their names.
Salutation for Informal and Formal letters
For Informal Letters
| (a) For Blood Relations (older) | Respected |
| (b) For Blood Relations (Youngers) | My dear, dear |
| (c) For Intimate Friends and Relatives | Dear, My dear |
For Formal Letters
| (a) Editors, Post Masters, police Officers | Sir/Madam |
| (b) Government Officials etc | Sir/Madam |
| (c) Principals and head of institutions | Respected Sir/Madam |
| (d) present or Prospective Employer | Sir/Madam |
| (e) shopkeeper, Businessmen, Manager | Sir/Madam |
| (f) Strangers and Acquaintances | Dear Sir/Madam or Dear Sir/Madam Ms |
Body
- The body is the most important elements of the letter. It can said to be the destination of journey as it lays the reason behind your writing. It includes the message the sender wants to convey. While the body of a personal letter can be long and detailed containing as many feelings, experiences, advices, news etc on a personal front built in formal letter it is best to use short, clear, logical paragraphs to state your subject.
- There can be three sub-parts of the body of a formal letter for letter drafting as follow, an introductory paragraph stating the main point, middle paragraph justifying the importance/need of writing with supporting points and a concluding paragraph restating the purpose and requesting for some action. The paragraphs of the body must be indented depending upon the style chosen.
- Be sure to skip a line between the salutation and introductory paragraph and also between the concluding paragraph and closure. Margins must be left on all four sides of the letter. It creates attractive appearance of the letter.
Concluding Line
- It comes at the end of the body of the letter, always begin as a new paragraph. It is determined by the writer’s relation with the addressee.
| (a) For friends | ‘with best regards’, ‘with best wishes’ |
| (b) for parents and elders | ‘with love and respect’, ‘with respect and affectionate regards’ |
| (c) For younger relatives | ‘with love’, ‘Best wishes’, ‘with best wishes’ |
| (d) For official letters | ‘thanking you’, ‘with best regards’ |
Complimentary closure
- It is a polite way to end your letter with respect. The traditional rule of Etiquette in Britain in that a formal letter starting with ‘Dear Sir/Madam’ must end with ‘Yours faithfully’, While a letter starting with ’Sir/Madam’ must end with ‘You sincerely’.
- In informal or personal letters, you may close the letter with ‘Yours Lovingly’, ‘Your truly’, ‘Your affectionately’ so on and depending upon your relation with receiver.
For Informal Letters
| (a) For friends and acquaintances | ‘Your sincerely’, ‘Sincerely yours’ |
| (b) for relatives and friends | ‘Yours affectionately’, ‘yours loving’ etc |
For Formal Letters
| (a) Principals, Headmasters etc | ‘yours obediently’ |
| (b) Editors, Government officials, Shopkeepers, private firms etc | ‘Yours faithfully’, ‘Your truly’ |
| (c) Strangers | ‘Your faithfully’ |
| (d) For employment from one official to another, complaints or requests to officials | ‘Your faithfully’ |
- Note: only the first letter of the first word in the complimentary closure is capitalized and all the other words are written/typed in small case.
Signature Line
- It is the last part of the letter where the sender signs off with his/her first and last name. The signature line may also included a second line in formal letters for the title/post of the sender, if appropriate.
Key Points of Better Letter Writing
- Selection of Correct Words: Words are the writer’s tools and the writer need to put the right word and right expression with precision. It should however be remembered that right words become relevant only in the right context. For example an emotional or flowery language has to be fully avoided in a business letter.
- To the Point content: Nothing more is harmful to good communication than confused state which may result in not conveying the exact point. Before writing a letter one should ne sure of what one wants to convey. All the facts and methodically. One should not be vague about one’s objective.
- Conciseness: Formal letters must be concise. In formal letters specially one must not write unnecessary sentences. To the point information or enquiry is prerequisite of a business correspondence. Long illustrations and elaboration must be avoided all costs.
- Courtesy: A letter reveals its writer’s personality and character. One must remain totally professional while writing a letter. Even while writing a complaint letter, care should be taken that it is couched in polite and civilized language. Good judgment determines what and how a point has to be conveyed.
- Correct Use of Punctuation Marks: Use of punctuation marks, use of capital letters, commas or colons is must to make our writing effective. Sometimes placement of comma or full stop at a wrong place may change the meaning of the sentence can steal the effectiveness of a good letter. Hence utmost attention should be paid to punctuation while writing.
- Style: The conversational style is the most suitable one for letter writing. It is best to write in a simple, clear style maintaining a logical sequence of ideas. Every sentence should grow out of the preceding one. There should be no abeupt jumping from one idea to the another.
Elements of a Letter at a Glance
Informal Letters
- Senders’ address
- Date
- Salutation
- Content required can be long and detailed
- Concluding line
- Complimentary closure
- Signature line
Formal Letters
- Senders’ address
- Date
- Receivers’ address
- Subject
- Salutation
- Content-Specific, to the point
- Concluding lines
- Complimentary closure
- Signature along with designation or title
Addressing an Envelope
- Addressing an envelope is important for those people who write letter, yet is not part of letter writing address property in cover of envelope will help you to deliver your envelope property to the destination.
- Postage and Address are two main elements of addressing an envelope. Here envelope format is also given for your better understanding.
Envelope Format
- The picture shows how an addressed envelope should look like. The horizontal lines represent lines of address.
Informal Letters
- Letters written to friends and relatives are called inform letters. They are also known as personal letters. They are usually written in an informal language. The tone and style are usually familiar and intimate, depending upon the level, of intimacy you have with the person you are writing to. Here one should not use formal and elaborate sentences, instead short and loosely connected sentences should be used, that will give the letter a natural look. You may also use conversation
- idioms and colloquial expressions. Contracted forms like won't, can't, I'll etc are also very common in personal letters.
- An informal letter expresses the personality of the person who writes it. It should have a friendly tone and the reader should be able to feel the sentiments and feelings as he/she goes through it.
- In informal letters we have covered following categories
- Personal Letters (family letters, letter to relatives, letters to elderly people, love letters are covered in this category.
- Social Letters (letter to friends, invitations, congratulatory letters and letters conveying good wishes letters of apology, letters offering condolence and expressing sympathies, thank you letters are covered in this category.
Purpose of Writing an Informal Letters
The main purposes of writing an informal letter are- to express feelings and emotions.
- to stay in contact with family and friends.
- to send invitations, replies, thanksgiving etc.
- to make personal complaints.
- to communicate by expressing sympathy, feeling
- congratulating someone etc.
How to Begin an Informal Letter?
- I received your letter yesterday and was delighted to know that.
- I have just received your letter and noted the contents.
- I got your letter and was delighted to know that you are coming.
- Everyone here was delighted to receive your much-awaited letter yesterday.
- Your delayed letter has been received by us just now and has removed our anxiety about well being.
How to End an Informal Letter?
You may use any of the following sentences as a closing line, if appropriate.- Please do write regularly
- Hope to get your reply soon.
- Take care of your studies and do write every week without fail.
- Rest is fine. Convey my regards to Mom.
- I expect you to write regularly in future.
Tips for Writing an Informal Letter or How To Write an Effective Informal Letter:
- While drafting an informal letter, observing the following tips may be beneficial
- Write as it you are speaking to the reader in person.
- Do not hesitate in adopting your personal style while writing to friends or relatives.
- Add Mr/Mrs/Ms' post the word Dear when writing to an
- Always start with a good/interesting news you want to share so that the reader feels positively associated with you.
- As there is no defined or set length for informal letters, try to keep it upto a page or a page and a half.
- Maintain a logical order while expressing ideas or replying to someone’s quires.
Sample of Informal Letter
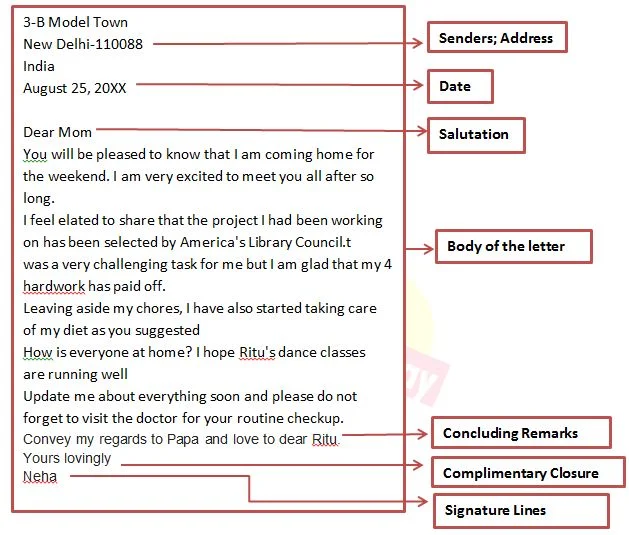
Parts of Informal Letter
- Senders' Address It includes house number, street/area pin code and country.
- Date It includes the date on which the letter is written.
- Salutation it is a customary greeting to the reader depending upon the intimacy between the writer and the reader.
- Body of the Letter It includes the text that embodies the purpose of writing. It may consist
- one or more paragraph Each paragraph focuses on a different idea/query/event.
- Concluding Remarks This part indicates that the letter is going to end. A concluding remark like 'love you' or 'missing you’ words can be written in this part.
- Complimentary Closure It is a warm subscription for the reader. It is also followed by the name of the writer. The first word in the complimentary closure always starts with capital letter.
- Signature Line It mentions the name of the writer. The handwritten signature goes above this line, below the closure.

